Arrays, as you must know from other programming languages, are used to store a collection of "things", and I am loosely saying "things" here. But here in JavaScript, arrays are a little different and they come with many valuable functions, and in this blog, we'll be looking at those!
Features of Arrays in JS 💫
- Arrays in JS are not primitive but are objects.
- Arrays are resizable in JS.
- They can also store data of different data types, so they are heterogeneous.
- They follow the indexing rule of 'start with 0'.
🔵 How to Use Arrays 🤔
There are many ways to declare and put data in Arrays, some of them are 👇
// Method 1: Using [] and Literals
let continent = [
"Europe",
"Asia",
"Africa",
"North America",
"South America",
"Australia",
"Antarctica",
];
// Method 2: Using constructor and new keyword
const skills = new Array("JS", "HTML", "CSS", "Tailwind", "Bootstrap");
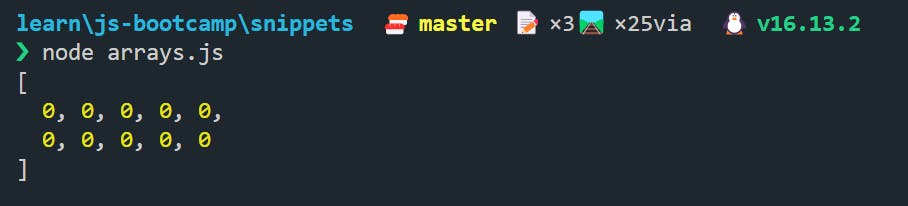
let score = Array(10);
score = score.fill(0);
console.log(score);
Now we have our array, but how to get stored data from the array?
🔵 Accessing Values 📦
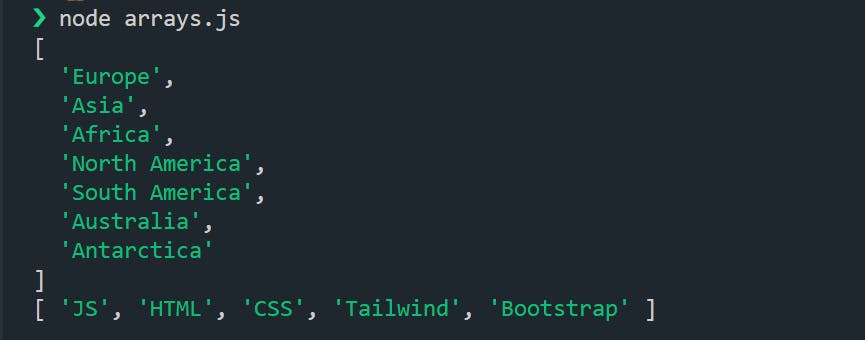
If we want to get the whole array, we can just give the array name
// accessing the whole array and printing it on terminal
console.log(continent);
console.log(skills);
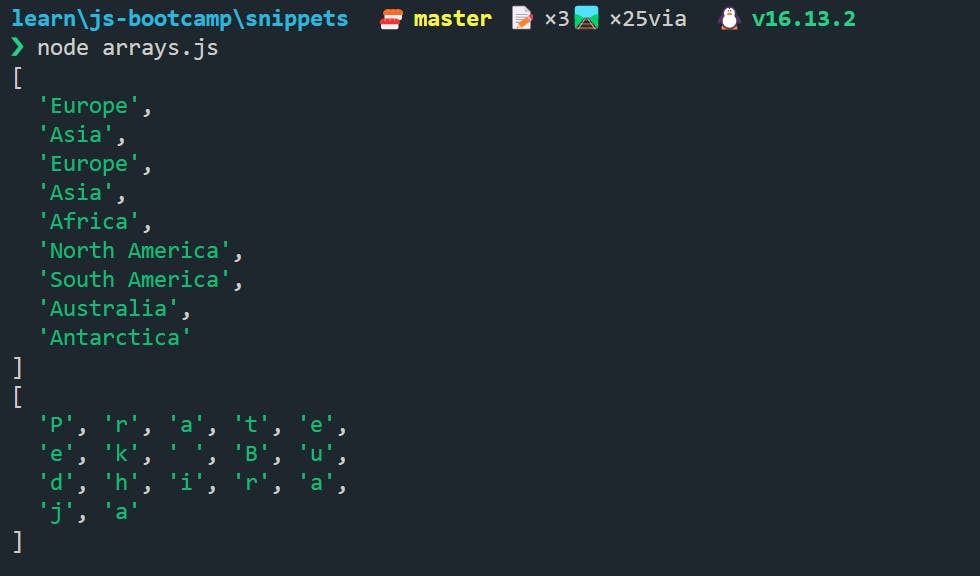
But if we want to get a particular element from the array, we can use [] to access a particular element. And as stated earlier, the index of an array starts from 0, therefore, the first element of the array will be at index 0, the second at index 1 and so on.
console.log(continent[1]);

🔵 Finding the Length 📏
We can find the length of an Array with .length
let continent = [
"Europe",
"Asia",
"Africa",
"North America",
"South America",
"Australia",
"Antarctica",
];
console.log("Array length is: ", continent.length);

🔵 New Array Instance 🆕
🍀 Now to create an Array from the previously created array, or from any iterable object, we can do it with Array.from()
// From a available array
let newContinentArray = Array.from(continent);
console.log(newContinentArray);
// From iterable object (string)
let arrayName = Array.from("Prateek Budhiraja");
console.log(arrayName);
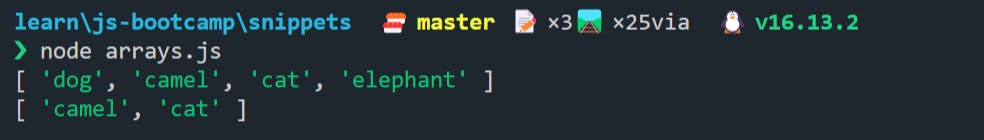
🍀 The slice() method returns a copy of a portion of an array into a new array object selected from start-to-end indexes. And the important thing to note here is that the end index is not inclusive.
const animals = ["ant", "dog", "camel", "cat", "elephant"];
console.log(animals.slice(1, 5));
console.log(animals.slice(2, -1));
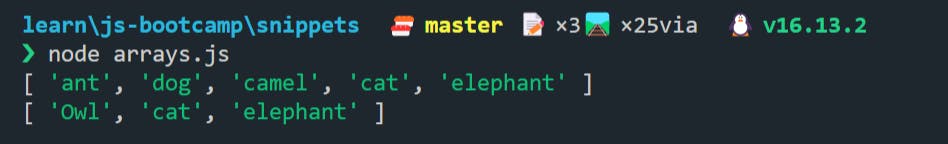
🍀 The splice() method changes the contents of an array by removing or replacing existing elements and/or adding new elements in place.
console.log(animals);
// syntax: splice(start, deleteCount, item1)
animals.splice(0, 3, "Owl");
console.log(animals);
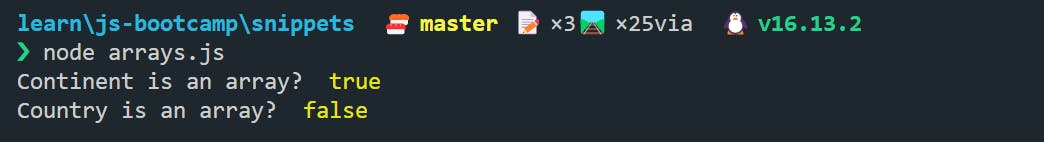
🔵 Check If Array ✔️
To check if the given name is an array or not, we have Array.isArray()
let continent = [
"Europe",
"Asia",
"Africa",
"North America",
"South America",
"Australia",
"Antarctica",
];
let country = "India";
console.log("Continent is an array? ", Array.isArray(continent));
console.log("Country is an array? ", Array.isArray(country));
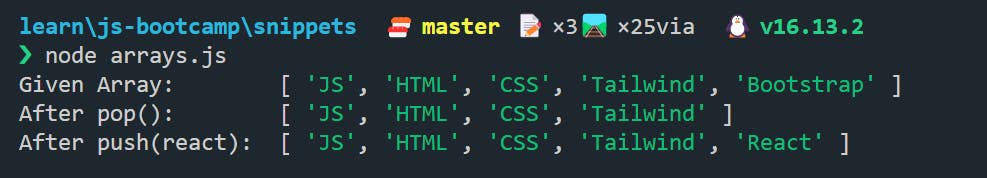
🔵 Adding and Removing elements from Array ➕➖
🍀 If we want to add/delete elements from the end of the Array (which is also recommended), then we can use push({element}) to insert elements to the array, and pop() to remove the element from the end of the array.
const skills = new Array("JS", "HTML", "CSS", "Tailwind", "Bootstrap");
console.log("Given Array: ", skills);
skills.pop();
console.log("After pop(): ", skills);
skills.push("React");
console.log("After push(react): ", skills);
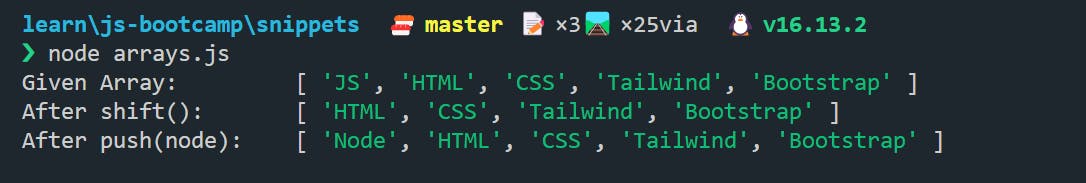
🍀 But if we want to insert or remove an element from the start of the array, then we can use unshift({element}) to insert an element at the start or shift(), to delete the element from start.
console.log("Given Array: ", skills);
skills.shift();
console.log("After shift(): ", skills);
skills.unshift("Node");
console.log("After push(node): ", skills);
🔵 Find Inside Array 🔎
If we need to find some elements from our array, we have many different functions to do that task.
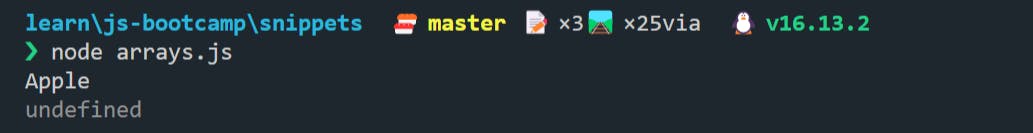
🍀 The find() method returns the first element in the provided array that satisfies the provided testing function. If no values satisfy the testing function, undefined is returned.
let fruitStock = ["Apple", "Pear", "Grapes", "Kiwi", "Cherry", "Pineapple"];
console.log(fruitStock.find((fruit) => fruit === "Apple")); // checking for "Apple"
console.log(fruitStock.find((fruit) => fruit === "Banana")); // checking for "Banana"
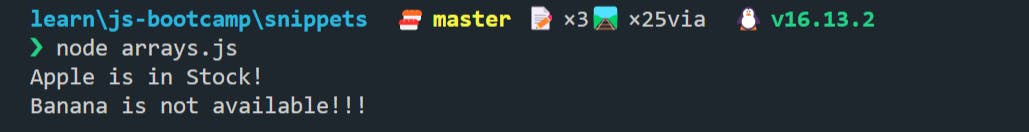
As it is just showing us undefined in the case of "Banana", we can use a good message by using:
console.log(
fruitStock.find((fruit) => fruit === "Apple")
? "Apple is in Stock!"
: "Apple is not available!!!"
);
console.log(
fruitStock.find((fruit) => fruit === "Banana")
? "Banana is in Stock!"
: "Banana is not available!!!"
);
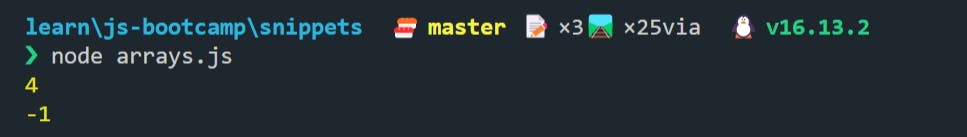
🍀 findIndex() returns the index of the first element in the array that satisfies the provided testing function, or -1 if no appropriate element was found.
It is like saying if something exists, where it is.
let fruitStock = ["Apple", "Pear", "Grapes", "Kiwi", "Cherry", "Pineapple"];
console.log(fruitStock.findIndex((fruit) => fruit === "Cherry"));
console.log(fruitStock.findIndex((fruit) => fruit === "Banana"));
find() and findIndex() finds the first occurrence of the element we provide, but if we want to get the last instance, we can use findLast() and findLastIndex().
🍀 findLast() will return the last instance of the element if found and findLastIndex() will returns the index of the last element in the array that satisfies the provided testing function, or -1 if no appropriate element was found.
let laptopInventory = ["HP", "HP", "Dell", "Apple", "Dell", "Apple"];
console.log(laptopInventory.find((laptop) => laptop === "Apple"));
console.log(laptopInventory.findIndex((laptop) => laptop === "Apple"));
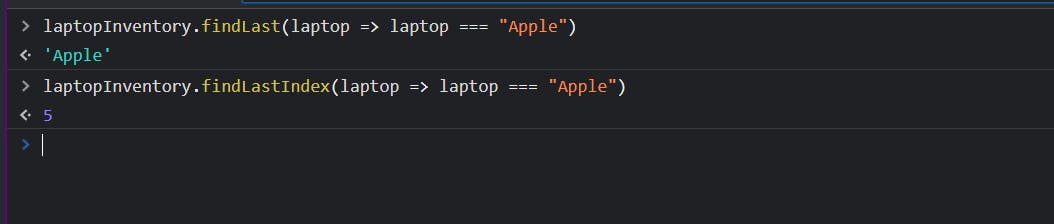
Notice, that it returned 5 instead of 3!
🍀 Another very useful function of Array is indexOf(), with this, we can get the index of any element which we specify. We even don't have to give a function to get the result. It returns the index of the element needed and returns -1 if the value is not in the array.
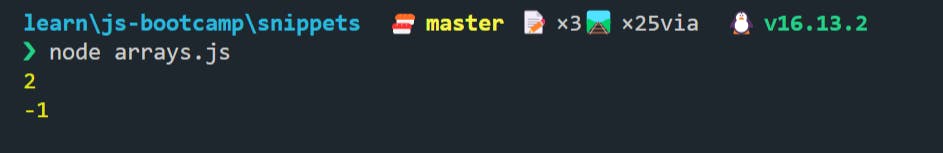
let continent = [
"Europe",
"Asia",
"Africa",
"North America",
"South America",
"Australia",
"Antarctica",
];
console.log(continent.indexOf("Africa"));
console.log(continent.indexOf("India"));
🔵 Sorting 📶
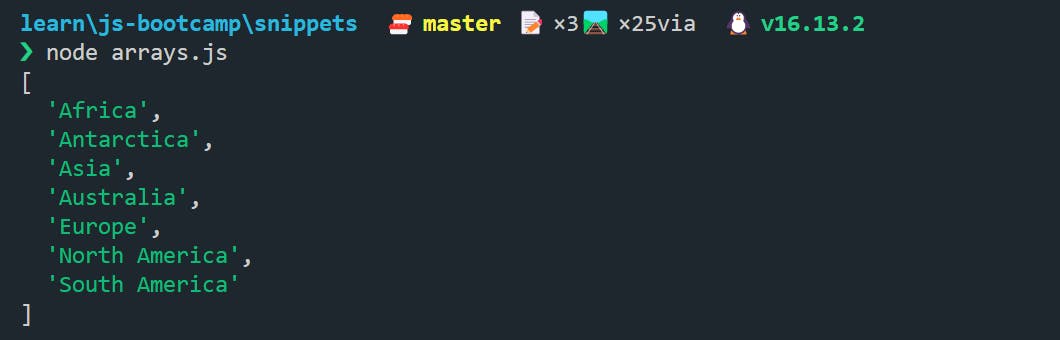
let continent = [
"Europe",
"Asia",
"Africa",
"North America",
"South America",
"Australia",
"Antarctica",
];
continent.sort();
console.log(continent);
🔵 Reverse
let numbers = [8, 4, 2, 1, -3];
console.log(numbers.reverse());

🔵 Map
The map function creates a new array and applies the provided function to each of its elements.
let numbers = [8, 4, 2, 1, -3];
let newNumbers = numbers.map((num) => Math.abs(num * 3));
console.log(numbers);
console.log(newNumbers);

🔵 Filter
The filter() creates a copy of a portion of a given array according to the condition provided.
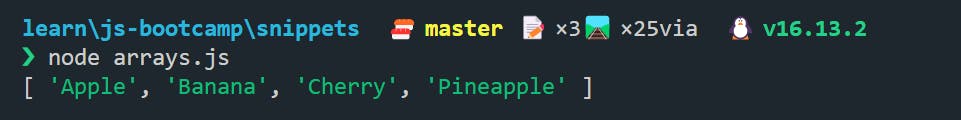
let foods = ["Apple", "Banana", "Cherry", "Pizza", "Pineapple"];
let fruits = foods.filter((food) => food !== "Pizza");
console.log(fruits);
I hope you learned something new from this blog, and you'll use some of these methods in your next project.
Happy Learning ✨